
6 月 . 26, 2024 02:40 Back to list
Glacial Acetic Acid Storage Incompatibilities Understanding and Mitigating Risks
Glacial Acetic Acid Storage Incompatibilities
Glacial acetic acid, also known as concentrated acetic acid, is a versatile chemical compound that finds extensive applications in various industries, from food and beverage production to pharmaceuticals and more. However, its storage presents unique challenges due to its reactive nature and the potential for incompatibilities with other materials. Proper storage of glacial acetic acid is crucial to maintain its purity, prevent degradation, and ensure safety. This article discusses the storage incompatibilities associated with glacial acetic acid and suggests best practices to mitigate these risks.
Firstly, it is imperative to recognize that glacial acetic acid is highly corrosive and can react vigorously with many metals, leading to the formation of flammable hydrogen gas. Thus, storing it in containers made from certain metals such as aluminum, zinc, magnesium, or alloys containing these metals can be dangerous. The acid can corrode these metals, resulting in contamination of the acid and potential hazardous situations. Instead, storage containers should be made from materials like polyethylene, polypropylene, or glass-lined steel, which are resistant to the corrosive properties of glacial acetic acid.
Temperature control is another critical aspect of glacial acetic acid storage. Exposure to high temperatures can cause the acid to decompose, forming byproducts that can affect its quality and safety. Therefore, it should be stored in a cool, well-ventilated area away from heat sources such as direct sunlight, heating equipment, or steam lines. It is recommended to keep the temperature below 25°C (77°F) to maintain the stability and integrity of the acid.
Moreover, glacial acetic acid is hygroscopic, meaning it can absorb moisture from the air. This can lead to a decrease in concentration and possible reactions with water, forming acetic acid solutions that may not meet the required specifications for certain applications This can lead to a decrease in concentration and possible reactions with water, forming acetic acid solutions that may not meet the required specifications for certain applications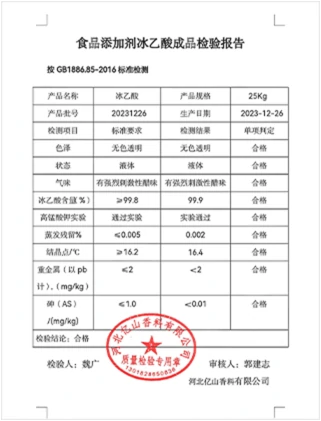 This can lead to a decrease in concentration and possible reactions with water, forming acetic acid solutions that may not meet the required specifications for certain applications This can lead to a decrease in concentration and possible reactions with water, forming acetic acid solutions that may not meet the required specifications for certain applications
This can lead to a decrease in concentration and possible reactions with water, forming acetic acid solutions that may not meet the required specifications for certain applications This can lead to a decrease in concentration and possible reactions with water, forming acetic acid solutions that may not meet the required specifications for certain applications glacial acetic acid storage incompatibilities. To prevent this, containers should be tightly sealed to minimize exposure to atmospheric moisture. Additionally, desiccants or drying agents can be used in the storage area to reduce humidity levels and protect the acid from moisture absorption.
Incompatibility with other chemicals is another concern during storage. Glacial acetic acid should be isolated from substances that could react violently with it, such as bases, oxidizing agents, or nitrates. Proper labeling and segregation of storage areas are essential to avoid mixing incompatible materials. Furthermore, any spillage or leakage should be cleaned immediately to prevent contact with other substances that might trigger a reaction.
Lastly, appropriate safety measures must be in place when handling and storing glacial acetic acid. Personnel should wear protective gear, including goggles, gloves, and acid-resistant clothing, to safeguard against splashes or accidental contact with the skin or eyes. Additionally, emergency equipment such as showers and eye wash stations should be readily accessible in case of accidents.
In conclusion, understanding and addressing the storage incompatibilities of glacial acetic acid is vital for maintaining its quality and ensuring safety. By using compatible materials for storage containers, controlling temperature and humidity, isolating it from incompatible substances, and implementing proper safety procedures, the risks associated with storing this powerful chemical can be significantly reduced. Adherence to these best practices allows for the effective and safe use of glacial acetic acid across various industries.
glacial acetic acid storage incompatibilities. To prevent this, containers should be tightly sealed to minimize exposure to atmospheric moisture. Additionally, desiccants or drying agents can be used in the storage area to reduce humidity levels and protect the acid from moisture absorption.
Incompatibility with other chemicals is another concern during storage. Glacial acetic acid should be isolated from substances that could react violently with it, such as bases, oxidizing agents, or nitrates. Proper labeling and segregation of storage areas are essential to avoid mixing incompatible materials. Furthermore, any spillage or leakage should be cleaned immediately to prevent contact with other substances that might trigger a reaction.
Lastly, appropriate safety measures must be in place when handling and storing glacial acetic acid. Personnel should wear protective gear, including goggles, gloves, and acid-resistant clothing, to safeguard against splashes or accidental contact with the skin or eyes. Additionally, emergency equipment such as showers and eye wash stations should be readily accessible in case of accidents.
In conclusion, understanding and addressing the storage incompatibilities of glacial acetic acid is vital for maintaining its quality and ensuring safety. By using compatible materials for storage containers, controlling temperature and humidity, isolating it from incompatible substances, and implementing proper safety procedures, the risks associated with storing this powerful chemical can be significantly reduced. Adherence to these best practices allows for the effective and safe use of glacial acetic acid across various industries.
 This can lead to a decrease in concentration and possible reactions with water, forming acetic acid solutions that may not meet the required specifications for certain applications This can lead to a decrease in concentration and possible reactions with water, forming acetic acid solutions that may not meet the required specifications for certain applications
This can lead to a decrease in concentration and possible reactions with water, forming acetic acid solutions that may not meet the required specifications for certain applications This can lead to a decrease in concentration and possible reactions with water, forming acetic acid solutions that may not meet the required specifications for certain applications glacial acetic acid storage incompatibilities. To prevent this, containers should be tightly sealed to minimize exposure to atmospheric moisture. Additionally, desiccants or drying agents can be used in the storage area to reduce humidity levels and protect the acid from moisture absorption.
Incompatibility with other chemicals is another concern during storage. Glacial acetic acid should be isolated from substances that could react violently with it, such as bases, oxidizing agents, or nitrates. Proper labeling and segregation of storage areas are essential to avoid mixing incompatible materials. Furthermore, any spillage or leakage should be cleaned immediately to prevent contact with other substances that might trigger a reaction.
Lastly, appropriate safety measures must be in place when handling and storing glacial acetic acid. Personnel should wear protective gear, including goggles, gloves, and acid-resistant clothing, to safeguard against splashes or accidental contact with the skin or eyes. Additionally, emergency equipment such as showers and eye wash stations should be readily accessible in case of accidents.
In conclusion, understanding and addressing the storage incompatibilities of glacial acetic acid is vital for maintaining its quality and ensuring safety. By using compatible materials for storage containers, controlling temperature and humidity, isolating it from incompatible substances, and implementing proper safety procedures, the risks associated with storing this powerful chemical can be significantly reduced. Adherence to these best practices allows for the effective and safe use of glacial acetic acid across various industries.
glacial acetic acid storage incompatibilities. To prevent this, containers should be tightly sealed to minimize exposure to atmospheric moisture. Additionally, desiccants or drying agents can be used in the storage area to reduce humidity levels and protect the acid from moisture absorption.
Incompatibility with other chemicals is another concern during storage. Glacial acetic acid should be isolated from substances that could react violently with it, such as bases, oxidizing agents, or nitrates. Proper labeling and segregation of storage areas are essential to avoid mixing incompatible materials. Furthermore, any spillage or leakage should be cleaned immediately to prevent contact with other substances that might trigger a reaction.
Lastly, appropriate safety measures must be in place when handling and storing glacial acetic acid. Personnel should wear protective gear, including goggles, gloves, and acid-resistant clothing, to safeguard against splashes or accidental contact with the skin or eyes. Additionally, emergency equipment such as showers and eye wash stations should be readily accessible in case of accidents.
In conclusion, understanding and addressing the storage incompatibilities of glacial acetic acid is vital for maintaining its quality and ensuring safety. By using compatible materials for storage containers, controlling temperature and humidity, isolating it from incompatible substances, and implementing proper safety procedures, the risks associated with storing this powerful chemical can be significantly reduced. Adherence to these best practices allows for the effective and safe use of glacial acetic acid across various industries. 